我的科研实验工作流
Table of Contents
当我们有了一个新的idea之后,就不得不通过一些实验对该想法进行验证。一般而言,验证包括以下三个主要流程:
- 寻找一个与当前idea最相关的源码,通过阅读该源码的文字描述(如论文)了解该源码的大体情况,之后通过该源码的说明文档配置环境并跑通该源码。
- 在跑通该源码的基础上,通过比较我的idea和该源码的idea的差距,确定出需要修改的部分,并进行修改。一般而言,我通过从运行入口处进入源码,大概找若干个文件即可找到最终地方目的地。在此过程中,常常需要通过了解一些变量的详细结构(我一般使用的时候添加print+运行来实现)。当正当地进行魔改之后,初步的idea代码就得到了。
实验当前代码,并比较和预期结果之间的差距(一般而言,一开始想的idea总是不那么合理的),大概经过四五次的探索,就会形成一个差不多的结果。在这个过程中,有一部分时间是在回顾自己所写的代码是否存在一些之前不知道的bug。
上述三个流程过后,可以说一个基本的代码就出现在眼前了。但这只是一个demo,如果是科研实验,还需要进行优化和标准化。优化是指:对现有模型,在实验所需要的指标上对代码进行优化。比如对于那些比较运行速度的代码,可能就需要看一看代码在哪里过于浪费时间,以及有没有什么进一步优化的空间。标准化则是指:实验需要产出一堆图和表格,因此需要写出一些shell脚本将这些实验在不同的实验条件下运行,甚至在相同的条件下多次重复运行。
笔者是在做NLP领域的一些工作,由于预训练模型技术的发展,当前的NLP基本是需要训练大规模的语言模型,然后进行一系列的评估的。在这样的一个领域下,不可避免地,会涌现出如下需求:
- 远程连接功能,具体而言,是连接到远程服务器上;
- 超参数调试的需求,用以选择最合适的超参数,以进行最终的实验;
shell脚本,需要通过shell脚本来批量化进行实验;
对于以上需求,笔者通过使用emacs来完成整体的上述工作流。在以上三个最主要的需求的基础上,还可以融入写paper、paper同步到oveleaf以供老师审阅、自定义和插入文本信息等诸多方面的遍历。包括本文,也是在emacs下的。下面逐一观察之:
1. 远程连接
可通过emacs的tramp实现,tramp是一个用起来挺不错的ssh工具,你甚至可以写一个简单的函数来管理你的服务器,然后把他绑定到对应的数字上。比如下面的配置:
;; add function (defun ssh-connect-41 () (interactive) (counsel-find-file "/ssh:username@xxx.xxx.xxx.41:/home/username/myfilepath") ) (general-create-definer my-space-leader-def :prefix "SPC" :states '(normal visual)) (my-space-leader-def "41" 'ssh-connect-41 )
2. 在后台运行当前buffer
(defun lz/running-current-bash-with-nohup () (interactive) (let* ((buffer-name (buffer-name)) (filepath (buffer-file-name)) (current-day-time (format-time-string "%F_%A_%T")) (filename (concat "running_" (s-replace ".sh" "" buffer-name))) (directory-path (nth 0(split-string filepath buffer-name))) (running-string (concat "nohup bash " buffer-name "> " current-day-time "-" filename ".log &")) (default-directory directory-path)) (shell-command running-string)) ) (defun lz/running-current-python-with-nohup () (interactive) (let* ((buffer-name (buffer-name)) (filepath (buffer-file-name)) (current-day-time (format-time-string "%F")) (filename (concat "running_" (s-replace ".sh" "" buffer-name))) (directory-path (nth 0(split-string filepath buffer-name))) (running-string (concat "nohup python " buffer-name "> " current-day-time "-" filename ".log &")) (default-directory directory-path)) (shell-command running-string)) ) (defun lz/running-current-python-with-nohup-env () (interactive) (let* ((buffer-name (buffer-name)) (filepath (buffer-file-name)) (current-day-time (format-time-string "%F")) (filename (concat "running_" (s-replace ".sh" "" buffer-name))) (directory-path (nth 0(split-string filepath buffer-name))) (running-string (concat "nohup python " buffer-name "> " current-day-time "-" filename ".log &")) (default-directory directory-path)) (setq envname (read-from-minibuffer "running environment? Ans:")) (setq full-string (concat (concat "export python=~/anaconda3/envs/" envname "/bin/python \n") "nohup $python " buffer-name "> " current-day-time "-" filename ".log &")) (shell-command (format "bash -c %s" (shell-quote-argument full-string)))) )
和运行ssh一样,可以把上述命令绑定到rs和rp(分别代表run shell和run python)。
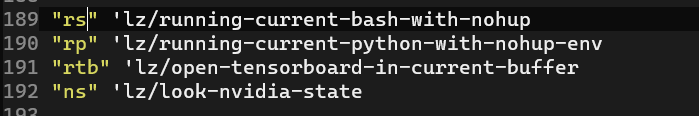
3. 其他操作
主要涉及到两个部分,一个是关注一下GPU有没有人在用(或者或哪一个没有人用),第二个是通过查看tensorboard的情况来调试超参数。
这两个任务都有对应的command,我把它简单封装一下,这样就不会每次都需要输入进去了:
;; tensorboard configuration. (defun lz/open-tensorboard-in-current-buffer() (interactive) (let* ((buffer-name (buffer-name)) (filepath (buffer-file-name)) (current-day-time (format-time-string "%F")) (directory-path (nth 0(split-string filepath buffer-name))) (default-directory directory-path) (host (nth 0 (split-string (nth 1 (split-string filepath "@")) ":")))) (setq tpath (read-from-minibuffer "tenserboard path is:" "\"./tensorboard\"")) (setq envname "dslz") (setq full-string (concat "source ~/anaconda3/bin/activate ~/anaconda3/envs/" envname "\n" "nohup tensorboard --host=" host " --logdir=" tpath ">>results.log &")) (shell-command (format "bash -c %s" (shell-quote-argument full-string)))) ) (defun lz/look-nvidia-state() (interactive) (let ((default-directory (nth 0 (split-string (buffer-file-name) (buffer-name))))) (shell-command "nvidia-smi") ) )